Publications
1. Towards Optimal Resource Allocation for Big Data Analytics
EDBT 2022; Link
We present a system for optimal resource allocation in big data systems that can predict performance impact for candidate resource allocations, for both new and past observed queries. We introduce the notion of a performance characteristic curve (PCC) as a parameterized representation that can compactly capture the relationship between resources and performance. To tackle the challenge of training data sparsity, we introduce a novel data augmentation technique to efficiently synthesize the entire PCC using a single run of the query. Lastly, we demonstrate the advantages of a constrained loss function coupled with GNNs, over traditional ML methods, for capturing the domain specific behavior through an extensive experimental evaluation over SCOPE big data workloads at Microsoft. Our results show that our fast and novel skyline simulation technique for data augmentation is sufficiently accurate, with a median percentage error in run time estimates of 9% on past jobs and our ML models can estimate the run time of jobs for different token counts well, before they have executed, with a median percentage error of 39% or less.
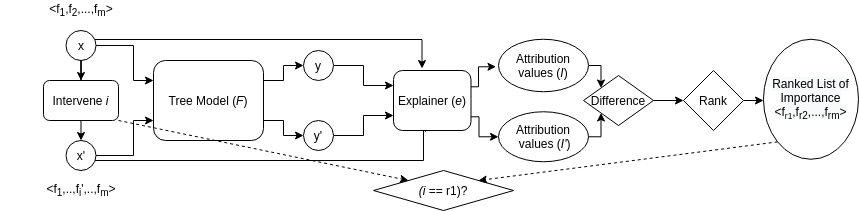
2. Evaluating Tree Explanation Methods for Anomaly Reasoning
CMAI ER 2020; link
We investigate the performance of two methods for explaining tree-based models: ‘Tree Interpreter (TI)’ and ‘SHAP TreeExplainer (SHAP-TE)’. Using a case study on detecting anomalies in job runtimes of applications that utilize cloud-computing platforms, we compare these approaches using metrics such as computation time, significance of attribution value, and explanation accuracy.’
US Patents
1. Optimizing job runtimes via prediction-based token alloc ation
Patent approved - 2022-03-31 link
2. Intelligent table suggestion and conversion for text
Patent applied - 2021-12-01
Pre-Prints
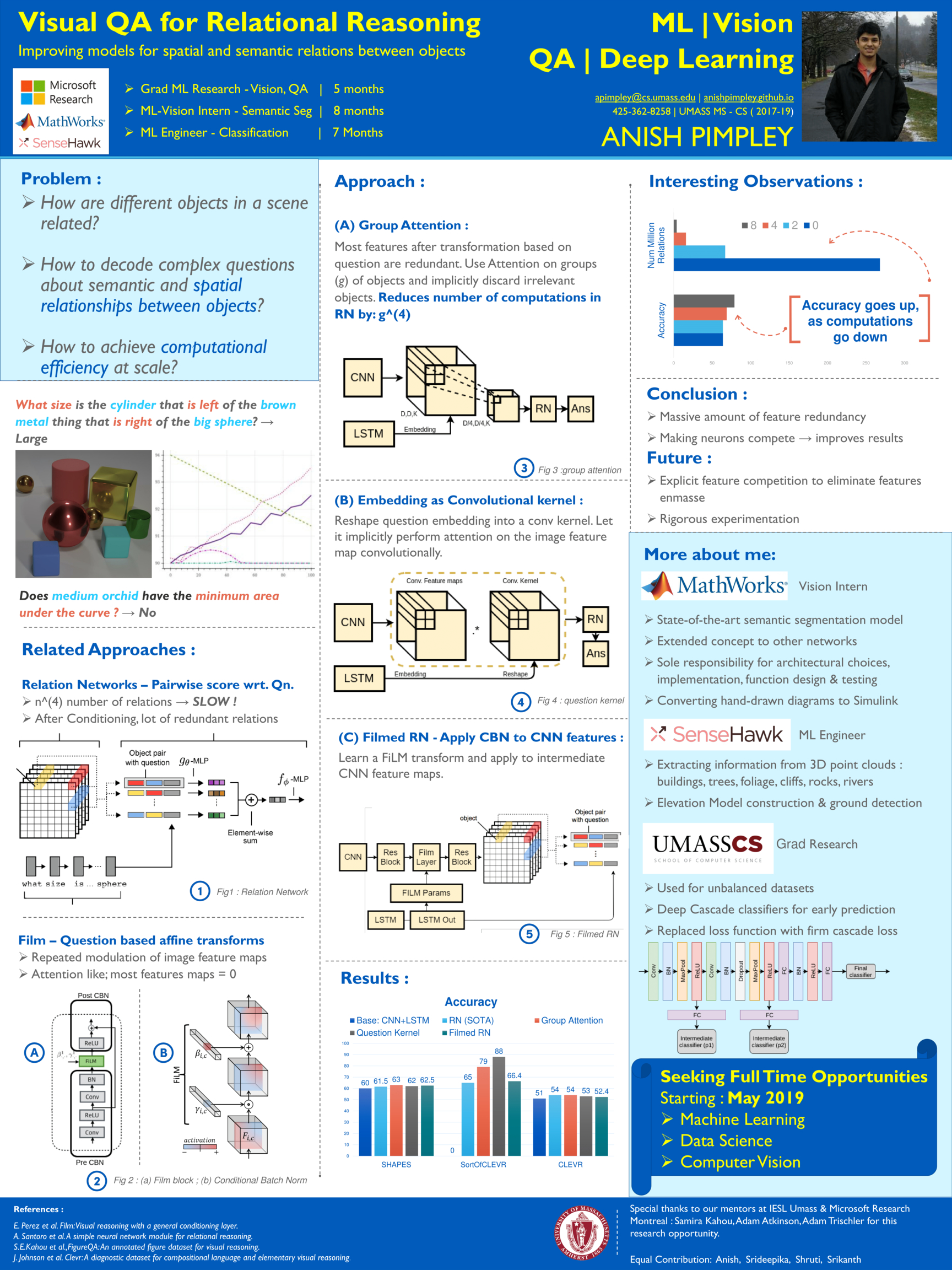
1. Maluuba FigureQA - Visual Question Answering for Relational Reasoning
Pre-Print 2018; link
We explore the task of relational reasoning (compositionality, physical interractions) via the specific problem of question answering in the space of plots and figures using the FigureQA dataset. We build on the ideas of task specific architectures such as Relation Networks and task generic architectures like FiLM to improve the state of the art performance on the FigureQA dataset.’
2. Survey of Multi-modal Emotion Recognition Approaches for Affective Computing
Pre-Print 2018; link
